Rwanda : target of 1 billion $ in digital FDI by 2035
Between 2013 and 2023, Rwanda attracted 819 million dollars in digital foreign direct investments (FDI). With the Digital FDI Initiative (DFDI), the country, which is relying more than ever on digital technology to accelerate its development, aims to surpass 1 billion dollars by 2035, focusing on connectivity, talent, and an investor-friendly environment. Analysis.

On January 3, 2025, the Digital Cooperation Organization (DCO) and the World Economic Forum (WEF) published a report titled “Digital FDI Initiative: Digital FDI-Enabling Project in Rwanda.” This document highlights the challenges and opportunities Rwanda faces in its quest to become a regional technology hub.
819 million $ in digital FDI in a decade
Between 2013 and 2023, Rwanda attracted 819 million dollars in foreign direct investments (FDI) in the digital sector. Software and IT services captured 45% of these investments, followed by communications with 37%. Despite these encouraging figures, the report highlights major obstacles, including limited internet connectivity, especially in rural areas, with a penetration rate of only 34.4% in January 2024. Furthermore, the lack of skilled professionals, regional competition, and insufficient support for startups are hindering the country’s digital development.
Digital at the heart of Vision 2050
Rwanda’s Vision 2050 aims to transform the country into an upper-middle-income economy by 2035, with a GDP per capita exceeding 4,036 dollars, and into a high-income economy by 2050, with a GDP per capita higher than 12,476 dollars. To achieve these objectives, the country is focusing on digital technology, considered an essential catalyst for economic and social development. As stated by Paul Kagame, President of the Republic of Rwanda: « We must work together to bridge the gaps in connectivity and digital transformation that still hinder access to opportunities. »
Solid foundations but ongoing efforts
In this context, the DCO and WEF report acknowledges Rwanda’s progress, particularly a favorable legal framework for foreign investments in the digital sector, exemplified by law no. 006/2021, which facilitates investments without foreign ownership restrictions. However, to compete with regional leaders like Kenya, which attracted 1.1 billion dollars in digital FDI in 2023, Rwanda must strengthen its infrastructure, simplify administrative procedures, and diversify the opportunities provided by its digital ecosystem.

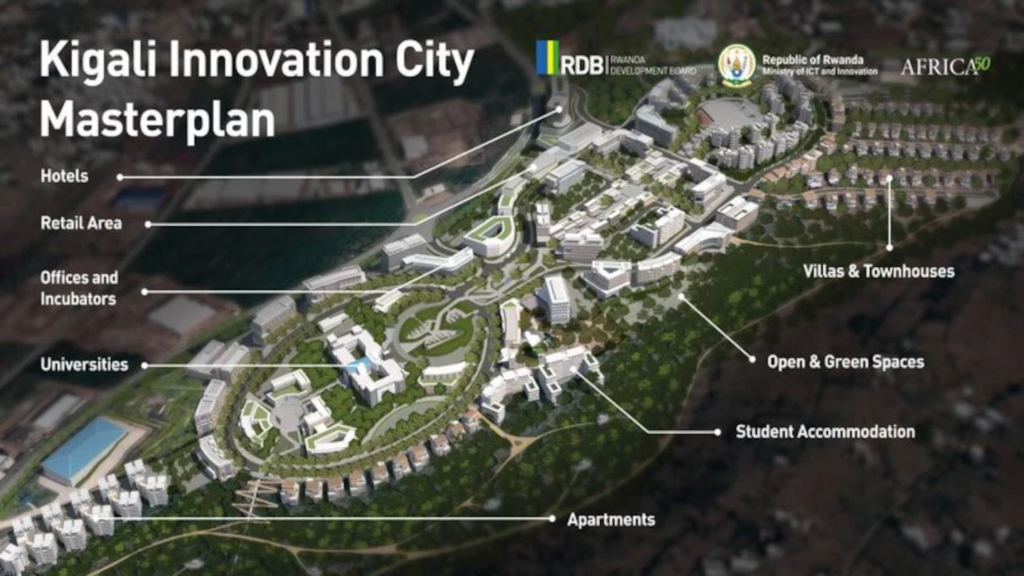
The country is implementing several strategic initiatives to overcome these obstacles and become a technology hub in East Africa. A key example is Kigali Innovation City (KIC), an ambitious project aimed at transforming the capital into a true technology center. The initiative, supported by a partnership with Africa50, plans to build an integrated technology ecosystem that will attract investors, startups, and international companies.
Artificial intelligence has the potential to promote social and economic equity when implemented thoughtfully

At the same time, Rwanda is investing in artificial intelligence (AI) through the Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR). This center, part of the World Economic Forum’s global network, aims to foster AI innovation to address some of the country’s most pressing challenges, such as improving education, managing natural resources, and modernizing agriculture. Paula Ingabire, Minister of Information and Communications Technology and Innovation, emphasizes the importance of this initiative: « Artificial intelligence has the potential to promote social and economic equity when implemented thoughtfully. »
A digital hub for East Africa
In this same dynamic, the establishment of Norrsken House in Kigali marks a turning point in the country’s digital entrepreneurial ecosystem. This innovation center aims to support local and international startups by offering coworking spaces, mentoring services, and funding opportunities to stimulate the growth of digital businesses. This type of initiative aligns with Rwanda’s desire to strengthen its position as a regional technology hub, facilitating collaborations between startups, businesses, and investors.
All of these initiatives aim to bridge the gaps in digital technology and position Rwanda as a key player in digital development in East Africa. The country is seeking to attract more foreign direct investments (FDI) in the digital sector, leveraging its strengths, including growing connectivity, a favorable legal framework, and its sustainable development ambitions. Rwanda hopes to become the region’s leading technology hub, a model of success in digital infrastructure and innovation.
For more information : World Economic Forum
Related topics :






